Description
Course type: Online; Self-Paced
Specialty: Respiratory
Language: English / Portuguese
Resources: Handbook
Level: Basic
Target: EMT
Modules: 5
Durations: 2 months
Time Effort: Up to 110 min per module
Certificate: Yes
Course Description
Proper management of a patient’s airway during emergency situations is of vital importance for EMTs. Because of this, a multitude of airway aids and devices are available for airway management. The respiratory complications associated are the common precursors of cardiac arrest. It is, therefore, crucial to detect problems in respiration in order to take action against cardiac arrest.
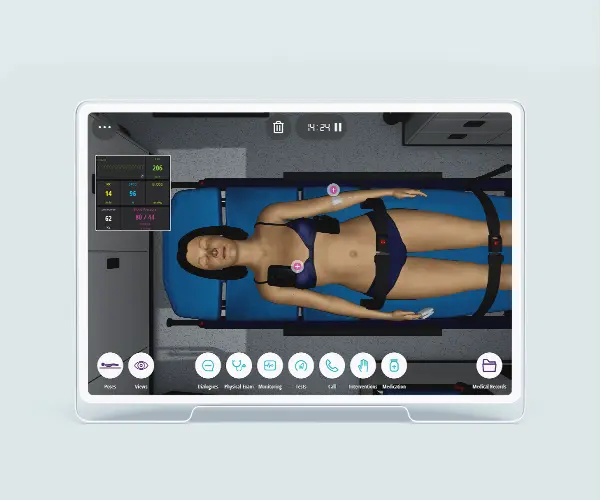
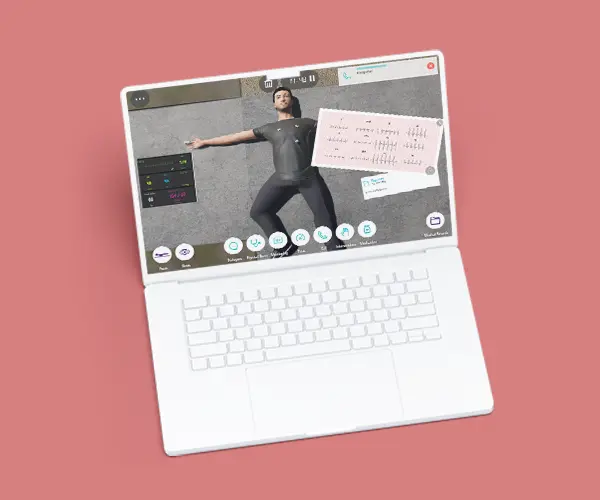
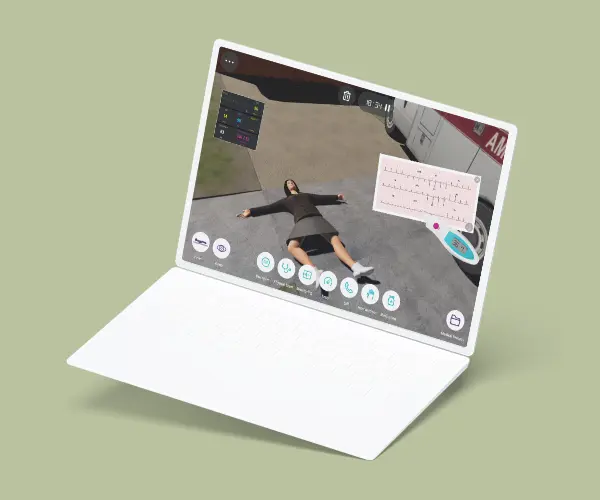
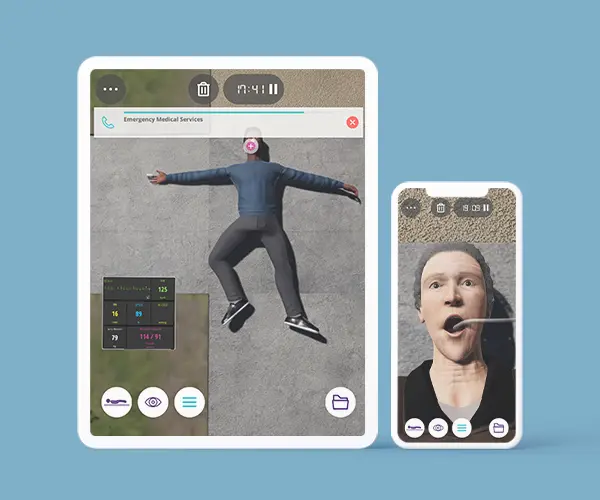
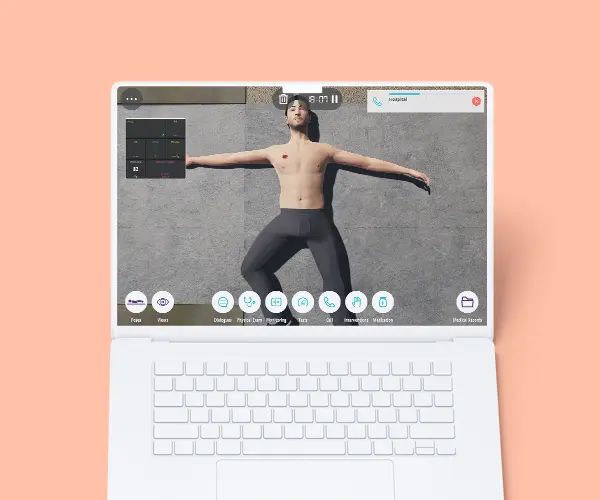
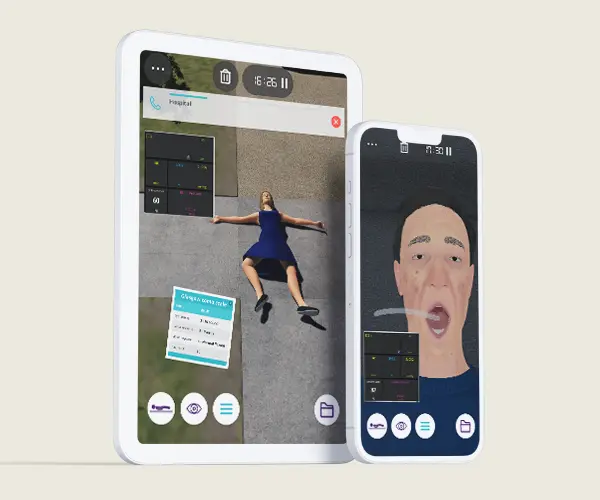
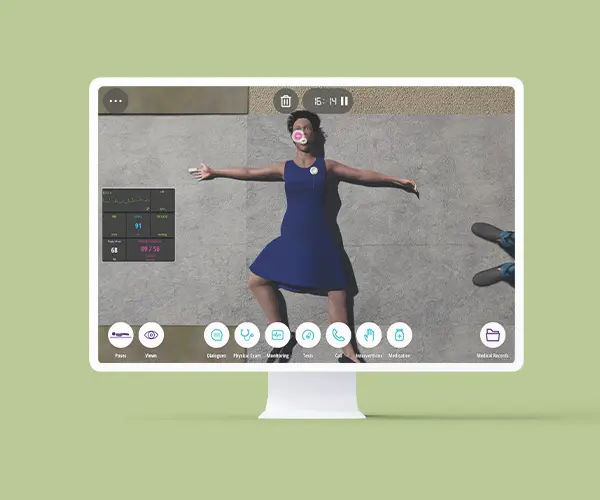
The Basic Airway and Breathing Management course is to describe basic oxygen delivery systems and basic equipment for ventilation. This course stands as a unique opportunity to develop the practical training of EMT teams or individuals through virtual patient scenarios either on the street or at home environments. Scenarios concern different areas in the scope of airway management and respiratory conditions for better performance in the decision-making process. Through this course, EMTs will develop their clinical reasoning in basic airway assessment and maneuvers in different respiratory conditions and their treatment.
Course Overview
- 5 Modules
• 5 virtual patient cases of a basic level of complexity. - Average Time to practice (per module)
• Clinical Scenario: 20 minutes per attempt (3 attempts: 60 minutes)
• Final attempt (if applicable): 20 minutes
• Multiple Choice Question: 5 minutes
• Feedback Area: 10 minutes
• Learning Objectives and Scientific References: 5 minutes - Online, Self-paced
2 months to complete the 5 modules at your own pace. - Certificate of Completion
Learning Objectives
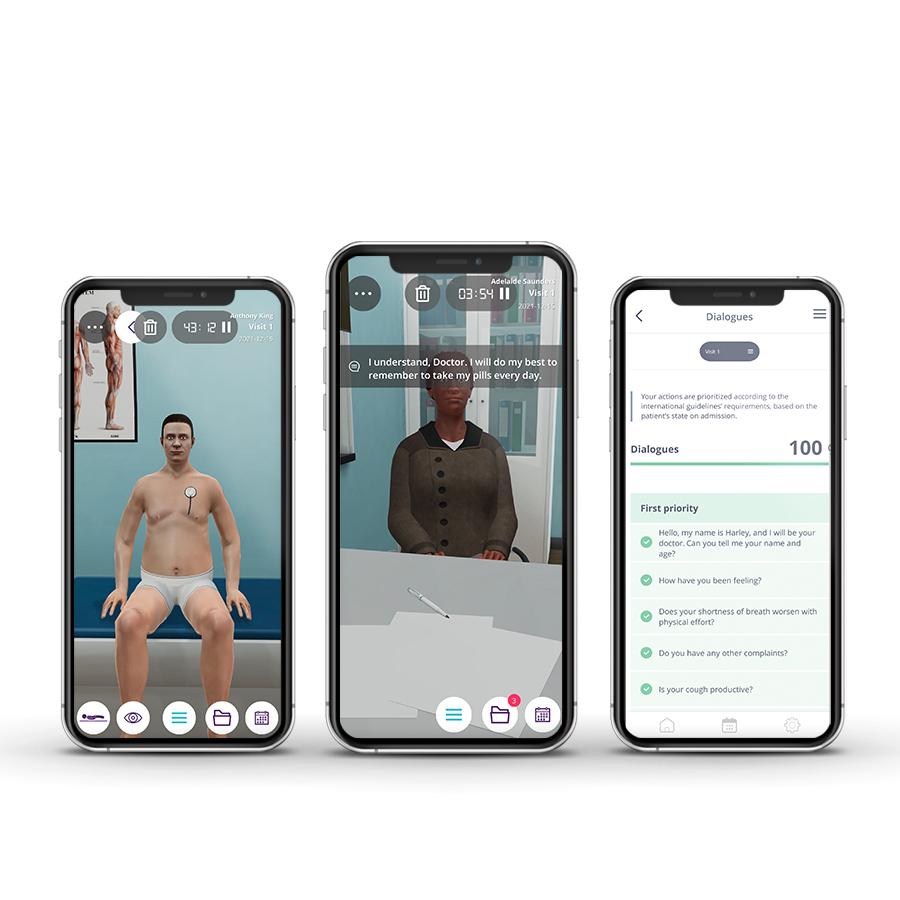
• Assess the security of care;
• Develop skills in the patient’s clinical history applying SAMPLE;
• Assess pain with OPQRST;
• Recognize the signs and symptoms of the airway obstruction;
• Ensure airway permeability through aspiration of secretions;
• Assess the patient’s respiratory condition, provide stabilization measures and request additional resources as needed;
• Call a higher level of emergency medical services for transport.
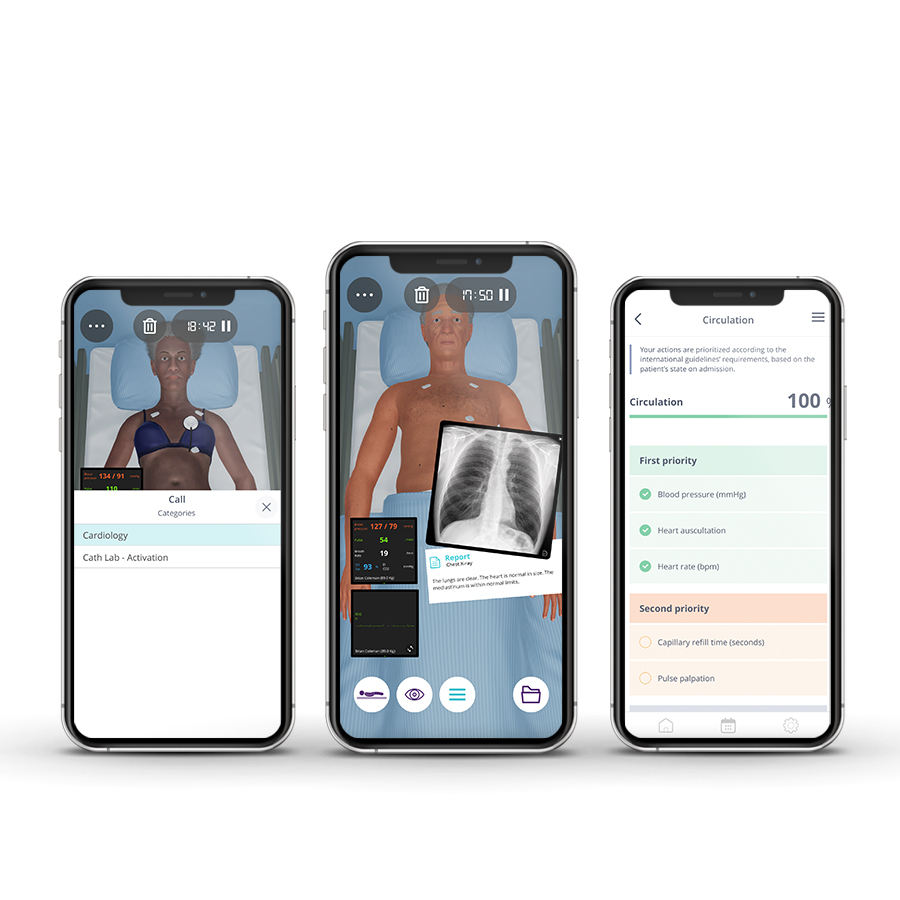
Clinical Competencies
Safety
• Universal safety measures procedures
• Promote patient safety
Airway and Breathing
• Airway – naso/oropharyngeal
• Oxygen therapy (nasal cannula; non-rebreather; high-flow mask)
• Pulse oximetry
• Suctioning – upper airway
Circulation
• Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
• Assess and interpret pulse (rate, rhythm and volume)
• Cardiac monitoring – 12-lead ECG
Medication- Routes
• Aerosolized / nebulized
• Intramuscular – auto-injector
• Intranasal – unit-dosed, premeasured
• Mucosal / Sublingual
• Oral
Module 1 – Collapse in front of house
Context: Airway management is important in both the pre-hospital and Emergency Room settings. The airway compromised is a health condition caused by a blockage in any of its segments. The blockage can be partial, complete, mild, or life-threatening.
Virtual Scenario: Charlotte was found collapsed in front of her house with breathing difficulties, her neighbor called Emergency Medical Services.
Module 2 – Call with airway complaints
Context: Approximately 20% to 30% of patients with lung cancer may develop a complication related to central airway obstruction, such as dyspnea, atelectasis, hypoxemia, hemoptysis, post-obstructive pneumonia, or respiratory distress.
Virtual Scenario: You respond to a call for a male with a chief complaint of dyspnea and unconsciousness.
Module 3 – Felt unwell when was running in the park
Context: Chronic inflammation of the airways causes the narrow of the airway, making it difficult to breathe. It is characterized by hyper-responsiveness of the airways, and bronchospasm is a symptom that limits most patients. A rapid and systematic approach is critical for a better prognosis of the patient.
Virtual Scenario: Jerry was running in the park in the middle of spring when he felt unwell.
Module 4 – Chest pain and shortness of breath
Context: Many health conditions can cause shortness of breath. The most common cause of acute dyspnea is related to respiratory infections. Different types of respiratory infections, including upper respiratory infections, pneumonia, acute bronchitis, and chronic bronchitis, can cause patients to develop shortness of breath.
Virtual Scenario: Willy lives with his wife. Today, after breakfast he felt ill with shortness of breath, cough with sputum, and chest pain. His wife called for an ambulance.
Module 5 – Experiencing progressive shortness of breath
Context: Increased fluid in the interstitial lung parenchyma space and alveolar space can be caused by cardiogenic and noncardiogenic pathologies. Evolution can be rapidly progressive and life-threatening.
Virtual Scenario: Jonas has recently retired and has been spending some time at home with his wife.
Authors and Speakers
With a multidisciplinary group of international clinical reviewers, Body Interact ensures a high standard of accuracy, diversity, and impact of its course.
Scientific References
- Cunningham C, Richard K. National Model EMS Clinical Guidelines. National Association of State EMS Officials. 2022; Version 3.
- National Association of State EMS Officials. National EMS Scope of Practice Model.2019; DOT HS 812 666