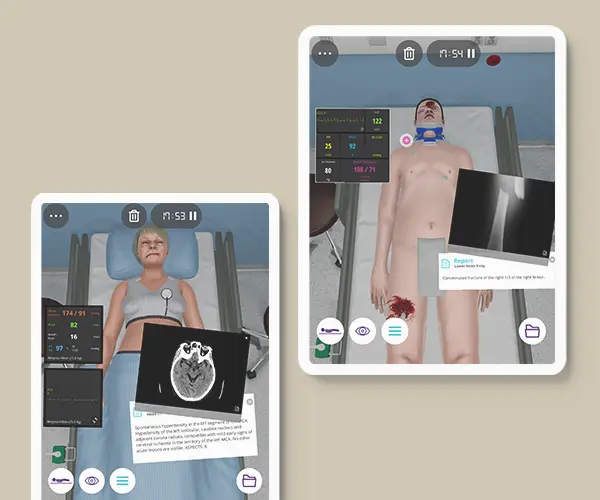
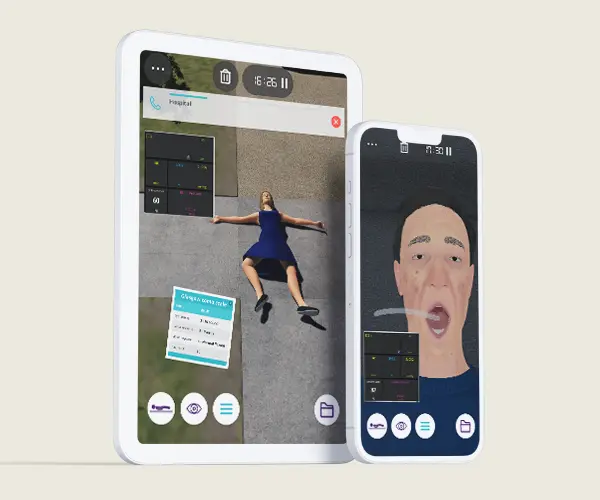
Description
Course type: Online; Self-Paced
Specialty: Geriatric
Language: English / Portuguese
Resources: Handbook
Level: Basic / Intermediate
Target: Nursing
Modules: 5
Durations: 2 months
Time Effort: Up to 110 minutes per module
Certificate: Yes
Course Description
The pediatric area presents unique challenges to nurses. The pediatric nursing care specialist in different areas plays a central role in dealing with each child. It is the nurse’s responsibility to help children deal with illness situations as well as medical procedures. A pediatric nurse deals not only with the child but also with all the anxieties and demands of the parents.
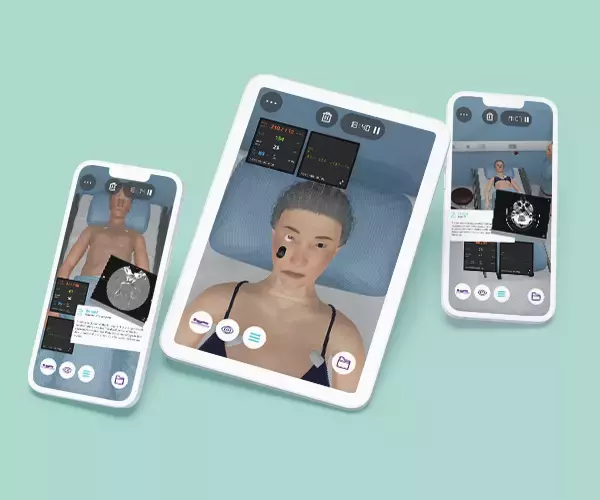
The Pediatric Nursing Care online course enables nurses to provide the best nursing care to pediatric virtual patients in an emergency room environment, encouraging a trusting relationship, with a holistic approach, between children and their families. This nursing course contains five clinical scenarios from different specialties (toxicology, respiratory, and urology, among others) with a debriefing video that follows the SBAR nursing communication.
Course Overview
- 5 Modules
• 5 virtual patient cases of an intermediate level of complexity - Average Time to practice (per module)
• Clinical Scenario: 20 minutes per attempt (3 attempts: 60 minutes)
• Final attempt (if applicable): 20 minutes
• Multiple Choice Question: 5 minutes
• Feedback Area: 10 minutes
• Learning Objectives and Scientific References: 5 minutes
• Debriefing Video: 10 minutes - Online, Self-paced
• You have up to 2 months to complete the 5 modules at your own pace. The course can be accessed through Body Interact at any time. - Certificate of Completion
• After completing the course, you will receive a Certificate of Completion that can be added to your CV or Resume.
Learning Objectives
• Recognize gastroenteritis and treat related symptoms (vomiting, dehydration, hypoglycemia, and fever)
• Identify and treat an asthma exacerbation according to medical indication
• Recognize intoxication conditions through interrogation to a family member and related signs and symptoms present in the child
• Identify and treat urinary tract infections according to medical indications
• Identify and treat a child with breathing difficulty and hypoxia due to pneumonia
Clinical Competencies
Safety
• Promote patient safety
• Universal precautions
• Refer to healthcare/ medical specialties
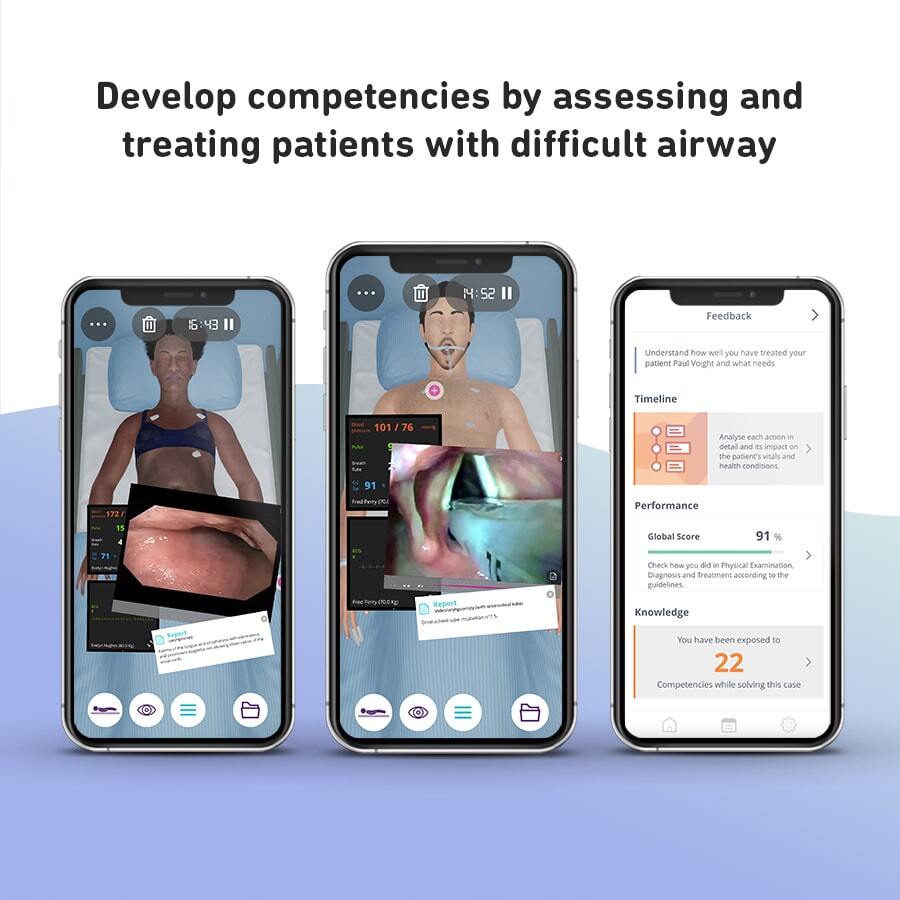
Airway
• Basic airway management
Breathing
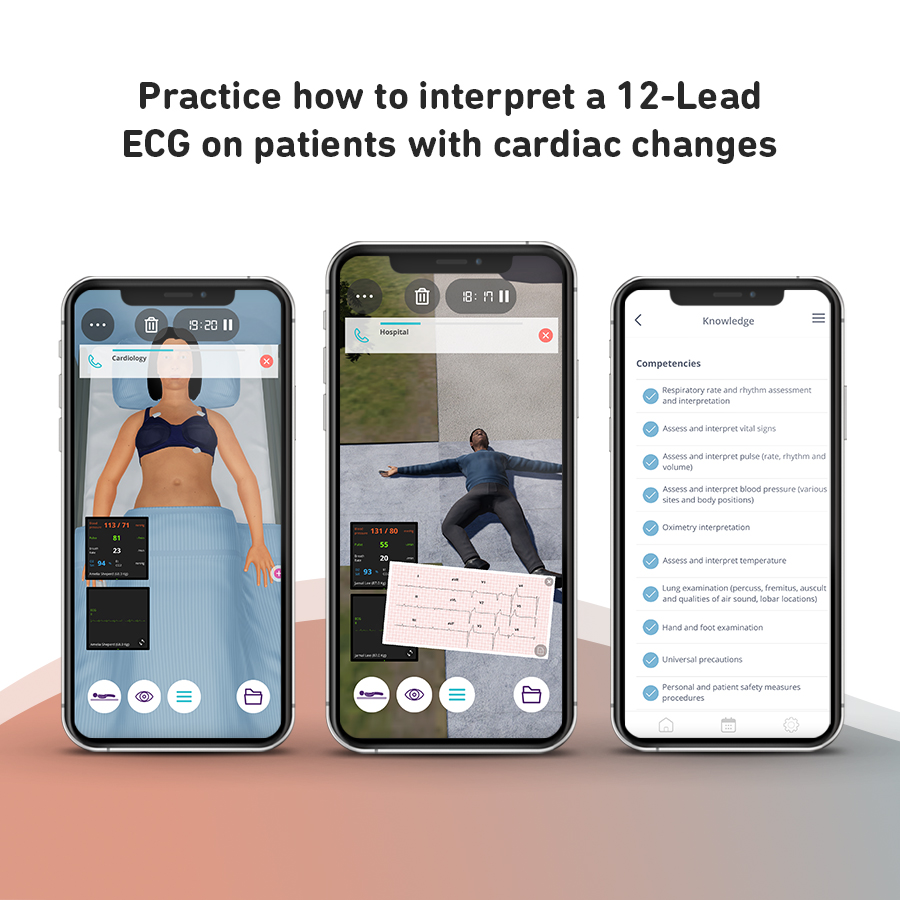
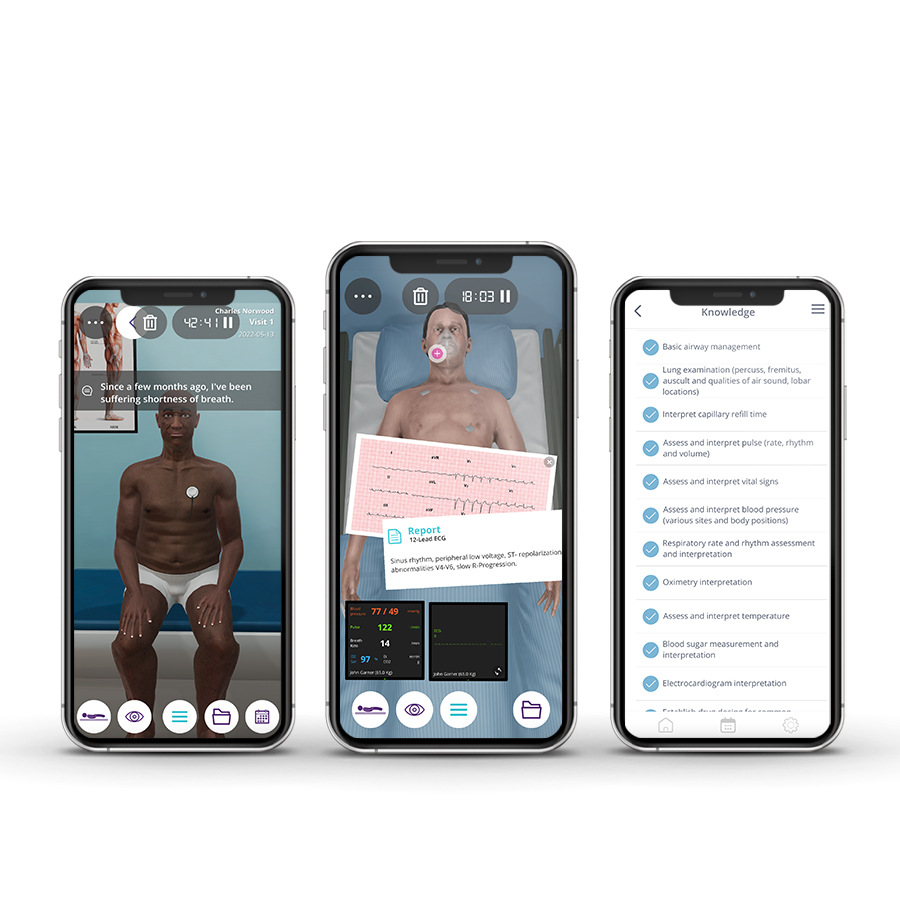
• Respiratory rate and rhythm assessment and interpretation
• Oximetry interpretation and O2 administration
• Thorax and Lung examination
• Chest x-ray interpretation
• Ventilator management
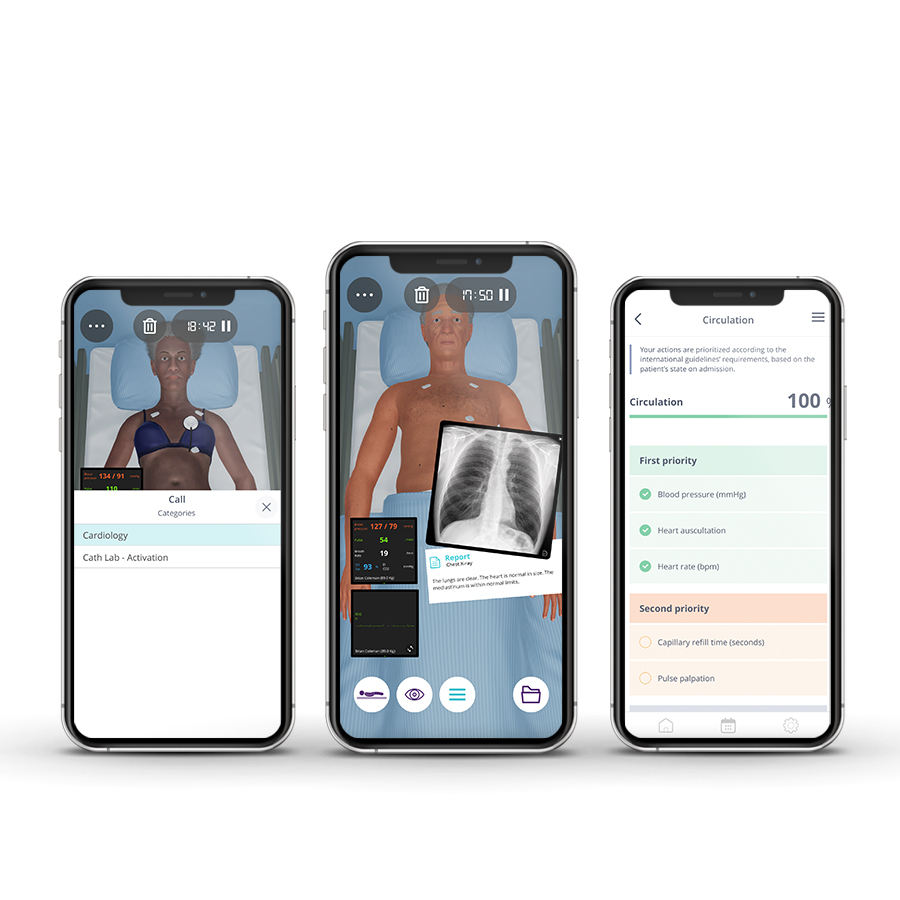
Circulation
• Assess and interpret pulse and blood pressure
• Detect heart murmurs and sounds: Identify S1 (tricuspid, mitral) and S2 heart sounds (pulmonary, aortic)
• Catheter management and establish drug dosing
• Interpret capillary refill time
Disability
• Blood sugar measurement and interpretation
• Pupillary and mental status assessment
Exposure
• Assess and interpret temperature
• Abdominal and extremity examination
• Laboratory tests interpretation: Cardiac enzyme; Liver function; Renal function; Hematocrit; Fluid/Electrolyte; Blood culture; Stool examination; Urinalysis
• Lesion qualities assessment (petechiae, urticaria, jaundice, vesicles, etc)
• Handle and position the patient body
Module 1 – Vomiting during two days
Context: Some common diseases in pediatrics can be lethal. Most complications occur from extreme dehydration resulting from a combination of severe diarrhea, vomiting, and not drinking enough fluids
Virtual Scenario: Arthur is brought to the Emergency Department by his mother after vomiting and diarrhea for two days. He has sunken eyes and is feeling weak since he cannot eat or drink water.
Module 2 – Breath effort while playing
Context: Frequent respiratory diseases in children are a serious problem causing wheezing, difficulty breathing, and coughing, and over a lifetime, it can cause permanent lung damage.
Virtual Scenario: Kiley was at her grandmother’s on what seemed a normal day, playing and interacting with the dog in the garden. Suddenly, her grandmother noticed her labored breathing and immediately brought Kiley to the hospital.
Module 3 – Playing with grandfather
Context: There are substances that can be toxic if a child swallows, inhales, or absorbs them through the skin. It is important to determine the causes and effects of poisoning in children and the necessary treatments.
Virtual Scenario: Malcom felt abdominal discomfort and was subsequently brought to the Emergency Department.
Module 4 – Irritability and frequent cry
Context: Certain children with an inability to communicate discomfort may show vague signs, irritability, and frequent crying. Screening for possible causes is essential to avoid severe complications.
Virtual Scenario: Sophia was in kindergarten when she started to become irritated and tearful for no apparent reason. Her mother is worried since she has a fever and noticed a strange smell in her diaper.
Module 5 – Fever during three days
Context: An inflammation of the lungs can be a serious complication that needs urgent treatment. A correct evaluation and early diagnosis are fundamental for the child’s prognosis..
Virtual Scenario: Melanie was born at 38-weeks and 4-days gestational age. Her mother denies a history of hospitalizations or outpatients visits for illness. She has had a fever for three days and started with breathing problems.
Authors
With a multidisciplinary group of international clinical reviewers, Body Interact ensures a high standard of accuracy, diversity, and impact of its course.
Body Interact has developed this course utilizing advanced medical simulation technology with virtual patients.
Scientific References
- Chung KF, Wenzel SE, Brozek JL, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. European Respiratory Journal. 2014;43(2):343-373.
- Fisher DJ, Steele RW. Pediatric Urinary Tract Infection. Medscape. 2019.
- Flerlage J, Engorn B. The Harriet Lane Handbook – a Manual for Pediatric House Officers. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders / Elsevier; 2015.
- Gilbert DN, Chambers HF, Saag MS, Pavia AT. The Sanford guide to antimicrobial therapy. 50th Ed. Antimicrobial Therapy; 2020.
- Hartman S, Brown E, Loomis E, Russel HA. Gastroenteritis in Children. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99(3):159-165.
- Hockenberry M, Rodgers C, Wilson D. Wong’s Essentials of Pediatric Nursing. 10th Ed. Elsevier; 2016.
- Rang NN, Chanh TQ, My PT, Tien TTM. Single-dose Intravenous Ondansetron in Children with Gastroenteritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Indian Pediatr. 2019;56(6):468-471.
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, British Thoracic Society. British Guideline on the Management of Asthma: A National Clinical Guideline. 2016.
- Skellett S, Hampshire S, Bingham R, Maconochie I, Mitchell S. European Paediatric Advanced Life Support. London: Resuscitation Council (UK); 2016.
- UNICEF, Save the Children, and Every Breath Counts. Every child’s right to survive: a 2020 agenda to end pneumonia deaths. 2020.
- Waseem, M. Pediatric Pneumonia. Medscape. 2020.
- Whyte LA, Al-Araji RA, McLoughlin LM. Guidelines for the management of acute gastroenteritis in children in Europe. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2015;100:308-312.